Moore4Medical is a European project led by Philips, comprised of a total of 65 partners, including universities, research institutes, hospitals, and private companies. The project aims to develop innovative microfabricated medical wearable devices and remote patient monitoring solutions, providing personalized healthcare services to empower patients and improve the quality of care.
About Moore4Medical
Moore4Medical is at the forefront of accelerating innovation in electronic medical devices. As observed in recent years: while the electronic consumer products industry is surging ahead with innovation, the development of medical devices has lagged behind. Moore4Medical is dedicated to closing this gap, exploring emerging medical applications, such as active implantable devices (bioelectronic medicines), organ-on-chip, drug adherence monitoring, smart ultrasound, radiation-free interventions, and continuous monitoring. These cutting-edge technologies promise to mitigate the rising costs of healthcare, reduce hospitalization, facilitate personalized therapies, and realize intelligent point-of-care diagnostic tools.
Moore4Medical is a European project led by Philips and is comprised of a total of 65 partners, including universities, research institutes, hospitals, and private companies. The project aims to develop innovative microfabricated medical wearable devices and remote patient monitoring solutions, providing personalized healthcare services to empower patients and improve the quality of care.
The consortium is focused on addressing some of the main challenges in modern healthcare, such as the need for more efficient and patient-centric systems, as well as wearable devices that seamlessly integrate with existing infrastructure. With an aging population and increasing demands for long-term remote care, Moore4Medical aims to provide cost-effective and sustainable wearable solutions that can deliver improved outcomes for patients.
Through the utilization of cutting-edge technology, and collaboration between expert companies in multiple fields, the project aims to create a range of intelligent medical devices, technologies, and monitoring systems. These innovations will enable real-time patient monitoring, and early detection of potential issues before they become serious, and provide clinicians with the necessary information to make informed decisions.
As the boundaries between the Pharmaceutical, MedTech, and Electronic Components and Systems (ECS) industries blur, new opportunities are emerging. Moore4Medical is addressing these opportunities in various domains:
- Implantable devices: Small implantable devices, termed “Bioelectronic Medicines,” will be utilized to treat a myriad of diseases, particularly chronic autoimmune diseases.
- Organ-on-chip: These devices mimic the basic functions of organs and will aid in developing personalized medicines, testing new drugs for safety, and reducing animal testing.
- Drug adherence: Miniature sensors and micropumps will ensure that expensive (biological) drugs are administered safely and correctly in home environments.
- Next-generation ultrasound: 3D ultrasound imaging based on MEMS ultrasound transducers in combination with AI algorithms will bring ultrasound diagnostics out of the hospital to semi-professionals, rural and remote areas, and even consumers.
- Towards X-ray-free surgery: Advanced optical tracking techniques and optical shape sensing will practically eliminate the need for ionizing X-ray imaging during minimally invasive interventions.
- Continuous monitoring: Wearable sensors and remote sensing technologies will reduce hospitalization, increasing patient comfort and reducing the cost of clinical trials in drug development.
Inpher Accelerates Moore4Medical Continuous Monitoring Initiative
Inpher specializes in secure (privacy-preserving) data analytics and machine learning. As part of the Moore4Medical project, Inpher is working on securing the remote bed monitoring system for detecting Atrial Fibrillation (A-fib) in hospitals, which collects patients’ data from different sensors placed in precise locations in the room and in the bed structure. Should the trained model identify atrial fibrillation, it will remotely alert clinicians or nurses as a preventive measure against potential strokes.
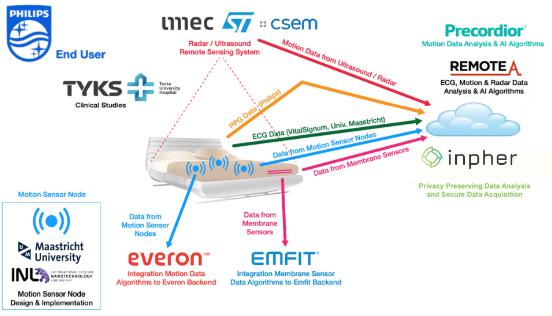
The data for the model training is collected from patients in hospitals in different countries.
Inpher is ensuring GDPR compliance through multiparty computation (MPC) coupled with other privacy-enhancing technologies (PETs) like Federated Learning (FL) and Fully Homomorphic Encryption (FHE). This advanced combination of PETs enables the secure, precise analysis of sensitive patient data coming from multiple sources without revealing any of the underlying private inputs.
Clinicians and researchers are now able to use the collected data to train algorithms and run machine learning models to detect A-fib and improve patient outcomes without risking the privacy of the individuals involved.
The Challenges in Developing a GDPR Compliant Remote Patient Monitoring System
One of the main challenges for healthcare organizations is ensuring that patient data that is collected, stored, and analyzed is both secure and GDPR compliant. To achieve this, organizations are implementing robust security processes and solutions to prevent unauthorized access, as well as ensuring that data is encrypted both in transit and at rest. An additional challenge being faced by researchers and clinicians is having the ability to efficiently and securely analyze the large volumes of varied data that is collected from patients using wearable devices and sensors. Maintaining the quality and integrity of the data throughout its collection, analysis, and storage is essential. Data must be accurate, complete, and free from bias to enable reliable model creation. Additionally, collecting data from multiple sources is a common requirement in many healthcare initiatives such as clinical research, population health management, and disease surveillance, and it comes with challenges. Patient data may contain sensitive information such as demographics, diagnoses, and treatments. The data collection coordination across different entities introduces additional people in the chain. On top of that, it must be ensured that data is consistent, compatible, interoperable, and standardized. It is quite clear that data collection introduces the risk of inadvertently sharing personal information that can identify individual patients, breaching their privacy. Addressing the above challenges requires the development of robust and secure systems that can efficiently aggregate and analyze diverse data, all while ensuring adherence to privacy regulations and safeguards for sensitive patient information.
Multiparty computation and more in general PETs, as utilized by Inpher in this project, enable a secure analysis of sensitive patient data from different sources without violating patient privacy or exposing data to unauthorized access and use.
Technologies Used by Inpher to Ensure Privacy of Patient Data
Multiparty computation and federated learning are two techniques used to enable the secure analysis of sensitive data without compromising the privacy of individuals.
Multiparty computation involves distributing data and computation across multiple parties in a way that no single party has access to the complete data set. Each party holds only a fraction of the data and performs computations only on its own data, ensuring that no individual gets access to any other party’s data. By exchanging cryptographic keys and sharing intermediate results instead of raw data, parties can jointly compute statistical averages and other algorithms without exposing any patient data to theft or misuse.
Federated learning is particularly important for wearable devices and distributed hardware. It allows models to be trained on data that is distributed across multiple devices without the need to transfer the data itself. Instead, the model is trained directly on-device, with data stored locally and not transmitted outside the device. The updated model is then sent to a central server, which aggregates the results from the different devices to create a global model without any individual device’s data being exposed.
Combining these two techniques with Fully Homomorphic Encryption (FHE), Inpher’s XOR proprietary technology provides a secure way to run machine learning models on distributed datasets without risking patient privacy. By minimizing the exposure of patient data XOR ensures that sensitive information remains confidential while still allowing for secure and effective data analysis across multiple locations.
Conclusion
The Moore4Medical Project ended in July, but it can still be celebrated as a great success thanks to Inpher and the other consortium partners’ contributions. It provides a glimpse into the possibilities of innovative Privacy Enhancing Technologies.
The development of a privacy-preserving remote bed monitoring system for atrial fibrillation detection is a significant accomplishment that has the potential to help healthcare institutions and patients alike.
Better model predictions, better patient outcomes, reduced costs for hospitalization and faster-informed decisions will dramatically improve all healthcare systems.
By ensuring GDPR compliance, the project also demonstrated an ethical and responsible approach to data handling in the healthcare industry that should be widely used.
Looking forward, the project’s success could serve as a reference for future innovations in remote healthcare monitoring, secure data sharing, and machine learning applications.
Inpher is pleased to announce its participation with Philips and 46 other partners in a new European project called Sustronics, with the aim of further advancements in sustainable and green electronics for healthcare.
In Sustronics, Inpher’s role will be to run secure predictive maintenance and to secure the pilot use case collecting patient data.
Inpher’s technology has reached its maturity and scalability in enabling secure and privacy-preserving collaborations between organizations. Rather than simply impacting the healthcare industry, the project’s achievements have far-reaching implications that extend beyond its boundaries.
As such, we are working on many other data collaboration use cases in sectors such as finance, government, telecommunication, and chip production.
Watch this video to learn more about this project. Discover how Inpher’s solutions can work for you by visiting here.

